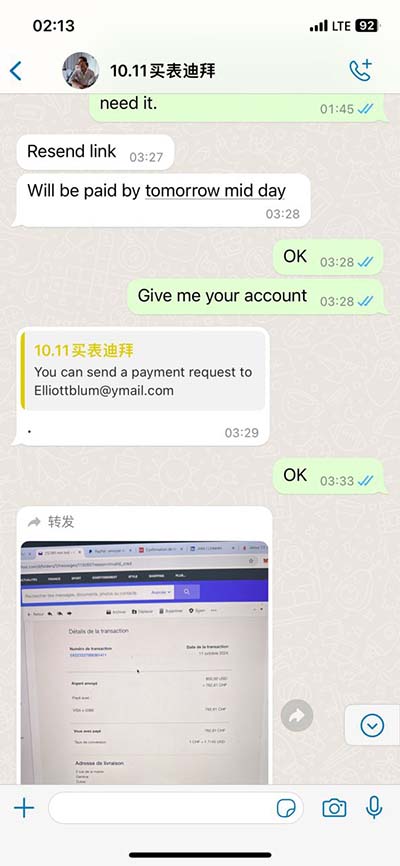
hermes king of chaldeans | who died in the chaldeans hermes king of chaldeans Nabopolassar declared himself king of Babylon and established the Neo-Babylonian Empire, also known as the Chaldean Dynasty. But Nabopolassar's rule was not limited to Babylon alone. He quickly expanded his control over other parts of Babylonia and . $578.00
0 · who were the chaldeans
1 · who died in the chaldeans
2 · the chaldeans in hebrew
3 · the chaldeans dynasty
4 · the chaldean empire in the bible
5 · chaldean empire wikipedia
6 · chaldea mesopotamia
7 · ancient chaldeans wikipedia
The Rolex Sea-Dweller, developed in 1967 but introduced to the general public in 1971, is a heavier-duty steel version of the Submariner, with a . See more
The Chaldeans and/or the Chaldean empire were a semi-nomadic tribe that lived in the southern portion of ancient Babylon and Mesopotamia along the Euphrates and Tigris rivers (in modern . Nabopolassar declared himself king of Babylon and established the Neo-Babylonian Empire, also known as the Chaldean Dynasty. But Nabopolassar's rule was not limited to Babylon alone. He quickly expanded his control over other parts of Babylonia and .The Chaldean dynasty, also known as the Neo-Babylonian dynasty and enumerated as Dynasty X of Babylon, was the ruling dynasty of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling as kings of Babylon from the ascent of Nabopolassar in 626 BC to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC. The dynasty, as connected to Nabopolassar through descent, was deposed in 560 BC by the Aramean officialChaldea was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BC, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was located in the marshy land of the far southeastern corner of Mesopotamia and briefly came to rule Babylon. The Hebrew Bible uses the term כשדים (Kaśdim) a.
who were the chaldeans
who died in the chaldeans
the chaldeans in hebrew
In order to secure the territory of Judah, Nebuchadnezzar brought Jehoiachin and Zedekiah, the two kings of Judah (in succession) and held them in Babylon. In keeping with Assyrian .
The Chaldeans were an intelligent and sometimes aggressive, warlike people. In 731 BC Ukinzer, a Chaldean, became king of Babylon; however, his reign was short-lived. A . The Chaldeans were an ethnic group that lived in Mesopotamia in the first millennium B.C. The Chaldean tribes started to migrate—from exactly where scholars aren't . Nebuchadnezzar was the most famous and important king of the Second Babylonian (or Neo-Babylonian or Chaldean) Empire, which fell to the Persian great king . Hermes was the ancient Greek god of trade, wealth, luck, fertility, animal husbandry, sleep, language, thieves, and travel. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and .
Nabopolassar declared himself king of Babylon and established the Neo-Babylonian Empire, also known as the Chaldean Dynasty. But Nabopolassar's rule was not limited to Babylon alone. He quickly expanded his control over other parts of Babylonia and worked to strengthen the empire's economy, infrastructure, and military.The Chaldean dynasty, also known as the Neo-Babylonian dynasty[2][b] and enumerated as Dynasty X of Babylon, [2][c] was the ruling dynasty of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling as kings of Babylon from the ascent of Nabopolassar in 626 BC to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC.
The Chaldeans and/or the Chaldean empire were a semi-nomadic tribe that lived in the southern portion of ancient Babylon and Mesopotamia along the Euphrates and Tigris rivers (in modern-day Iraq).The Chaldean states in Babylonia during the 1st millennium BC. Chaldea [1] (/ k æ l ˈ d iː ə /) was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BC, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. [2] Semitic-speaking, it was located in the marshy land of the far southeastern . Merodach-Baladan died, and after a period of time, a certain Chaldean by the name of Mushezib-Marduk proclaimed himself king of Babylon. Sennacherib, after an arduous battle, laid siege to Babylon and defeated it in 689.In order to secure the territory of Judah, Nebuchadnezzar brought Jehoiachin and Zedekiah, the two kings of Judah (in succession) and held them in Babylon. In keeping with Assyrian practice, the " New Babylonians," or Chaldeans forced a large part of the Jewish population to relocate.
The Chaldeans were an ethnic group that lived in Mesopotamia in the first millennium B.C. The Chaldean tribes started to migrate—from exactly where scholars aren't sure—into the south of Mesopotamia in the ninth century B.C. Nebuchadnezzar was the most famous and important king of the Second Babylonian (or Neo-Babylonian or Chaldean) Empire, which fell to the Persian great king Cyrus the Great in 539 B.C. The Chaldeans were an intelligent and sometimes aggressive, warlike people. In 731 BC Ukinzer, a Chaldean, became king of Babylon; however, his reign was short-lived. A few years later Merodach-Baladan, also a Chaldean, became king over Babylon. Hermes was the ancient Greek god of trade, wealth, luck, fertility, animal husbandry, sleep, language, thieves, and travel. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger. In that position, he came to symbolise the crossing of boundaries in his role as a guide between the two realms of .
Nabopolassar declared himself king of Babylon and established the Neo-Babylonian Empire, also known as the Chaldean Dynasty. But Nabopolassar's rule was not limited to Babylon alone. He quickly expanded his control over other parts of Babylonia and worked to strengthen the empire's economy, infrastructure, and military.The Chaldean dynasty, also known as the Neo-Babylonian dynasty[2][b] and enumerated as Dynasty X of Babylon, [2][c] was the ruling dynasty of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling as kings of Babylon from the ascent of Nabopolassar in 626 BC to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC.
The Chaldeans and/or the Chaldean empire were a semi-nomadic tribe that lived in the southern portion of ancient Babylon and Mesopotamia along the Euphrates and Tigris rivers (in modern-day Iraq).
rolex milgauss with a suit
The Chaldean states in Babylonia during the 1st millennium BC. Chaldea [1] (/ k æ l ˈ d iː ə /) was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BC, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. [2] Semitic-speaking, it was located in the marshy land of the far southeastern . Merodach-Baladan died, and after a period of time, a certain Chaldean by the name of Mushezib-Marduk proclaimed himself king of Babylon. Sennacherib, after an arduous battle, laid siege to Babylon and defeated it in 689.In order to secure the territory of Judah, Nebuchadnezzar brought Jehoiachin and Zedekiah, the two kings of Judah (in succession) and held them in Babylon. In keeping with Assyrian practice, the " New Babylonians," or Chaldeans forced a large part of the Jewish population to relocate. The Chaldeans were an ethnic group that lived in Mesopotamia in the first millennium B.C. The Chaldean tribes started to migrate—from exactly where scholars aren't sure—into the south of Mesopotamia in the ninth century B.C.
Nebuchadnezzar was the most famous and important king of the Second Babylonian (or Neo-Babylonian or Chaldean) Empire, which fell to the Persian great king Cyrus the Great in 539 B.C. The Chaldeans were an intelligent and sometimes aggressive, warlike people. In 731 BC Ukinzer, a Chaldean, became king of Babylon; however, his reign was short-lived. A few years later Merodach-Baladan, also a Chaldean, became king over Babylon.
red bank rolex
presidential rolex value
red rolex arabic numerals
the chaldeans dynasty
1950s – 1960s. The vast majority of the Omega Constellation watches from the early 1950s and 1960s followed the same design language and featured the now-iconic pie .
hermes king of chaldeans|who died in the chaldeans